Setup OpenVPN On CentOS Via Command Line
This tutorial explains how to set up OpenVPN on CentOS Linux through Command Line Interface, CLI.
If you want to set up the VPN through the Network Manager on CentOS Desktop version, find the setup guides here.
Step #1: Update the CentOS packages list and install Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) by running the following commands.
sudo yum update -y sudo yum install epel-release -y
Step #2: Now update the packages list again.
sudo yum update -y
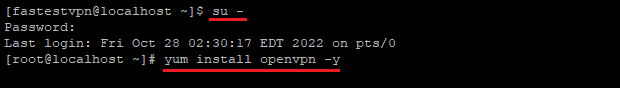
Step #3: Switch to the root user by entering su – and install OpenVPN.
yum install openvpn -y
Step #4: Enter into the OpenVPN directory and download FastestVPN’s OpenVPN server config files by running these commands.
cd /etc/openvpn sudo wget http://support.fastestvpn.com/download/fastestvpn_ovpn/ -O fastestvpn_ovpn.zip
Note: If it says that “wget command not found” then install it by entering sudo yum install wget and run the above command again.
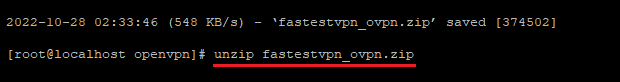
Step #5: Unzip the downloaded files.
unzip fastestvpn_ovpn.zip
Note: If it says that “unzip command not found” then install unzip by entering sudo yum install unzip and follow Step # 5 again.
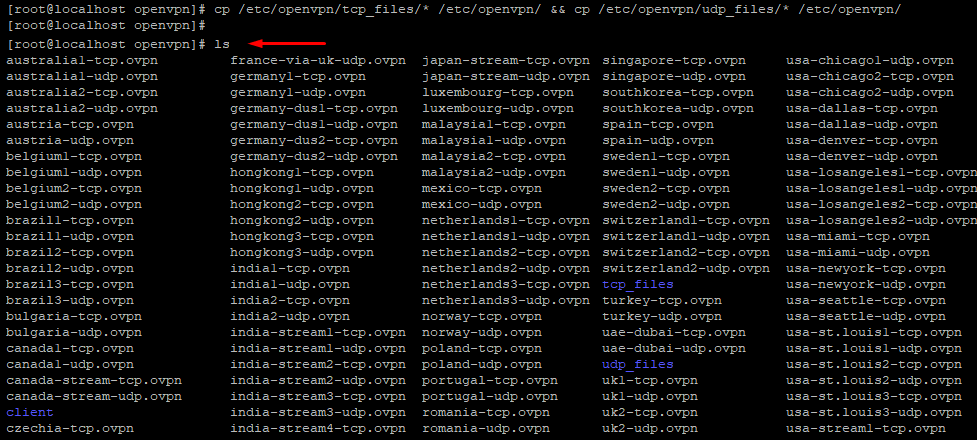
Step #6: Now copy the unzipped server files into the OpenVPN directory.
cp /etc/openvpn/tcp_files/* /etc/openvpn/ && cp /etc/openvpn/udp_files/* /etc/openvpn/
Step #7: Enter ls so all the FastestVPN server files in the directory will be listed.
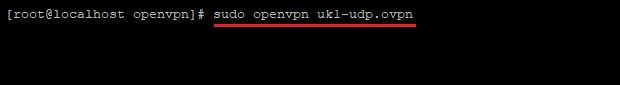
Step #8: Connect to your desired TCP or UDP VPN server by entering sudo openvpn [your desired server name]
For example:
sudo openvpn uk1-udp.ovpn
Step #9: It will require you to enter your credentials. Enter your FastestVPN Username and then Password.
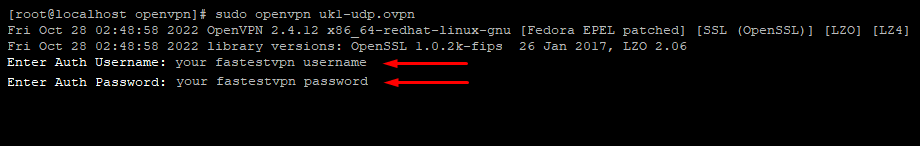
Step #10: Once the logs show “Initialization sequence completed” that means the VPN connection has been established.
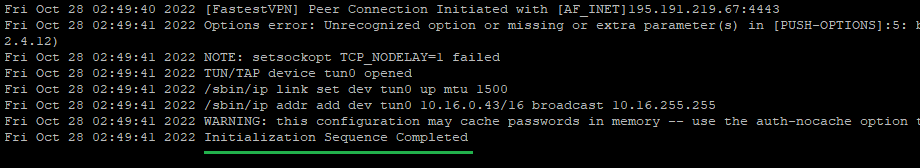
To disconnect from the VPN, press Ctrl+C in the same command line session, or in another session, enter sudo pkill openvpn
To connect to another server, enter into the OpenVPN directory and follow Steps # 7 to 9.